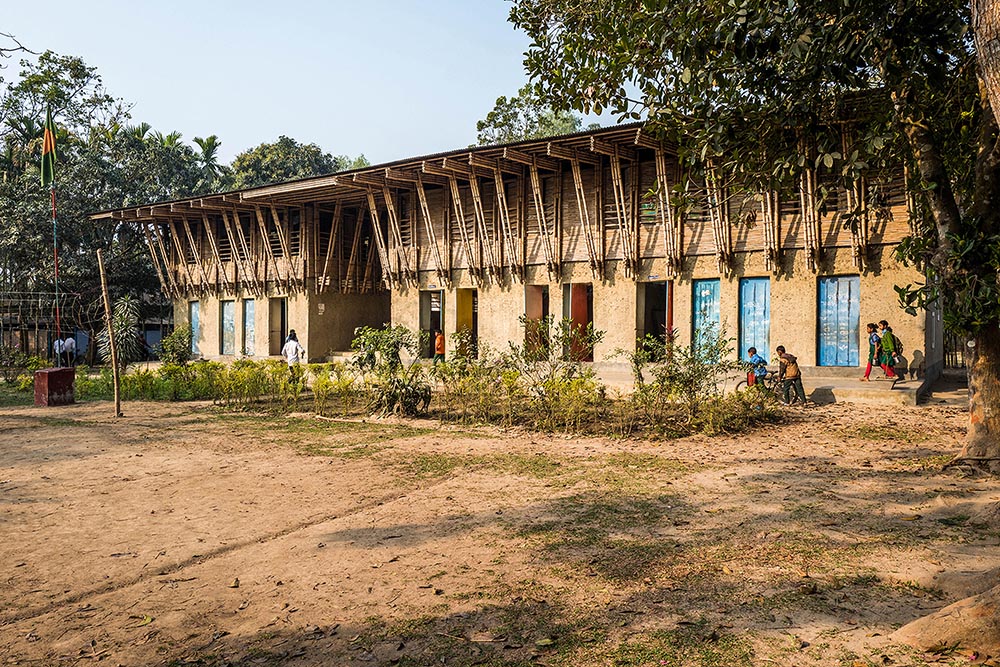
METI Handmade School
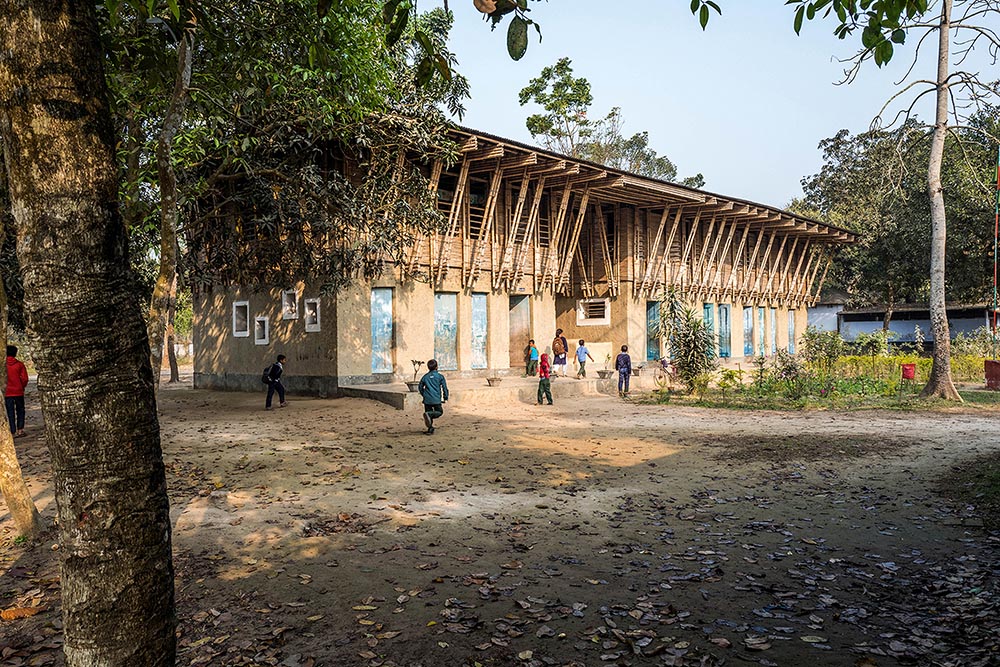
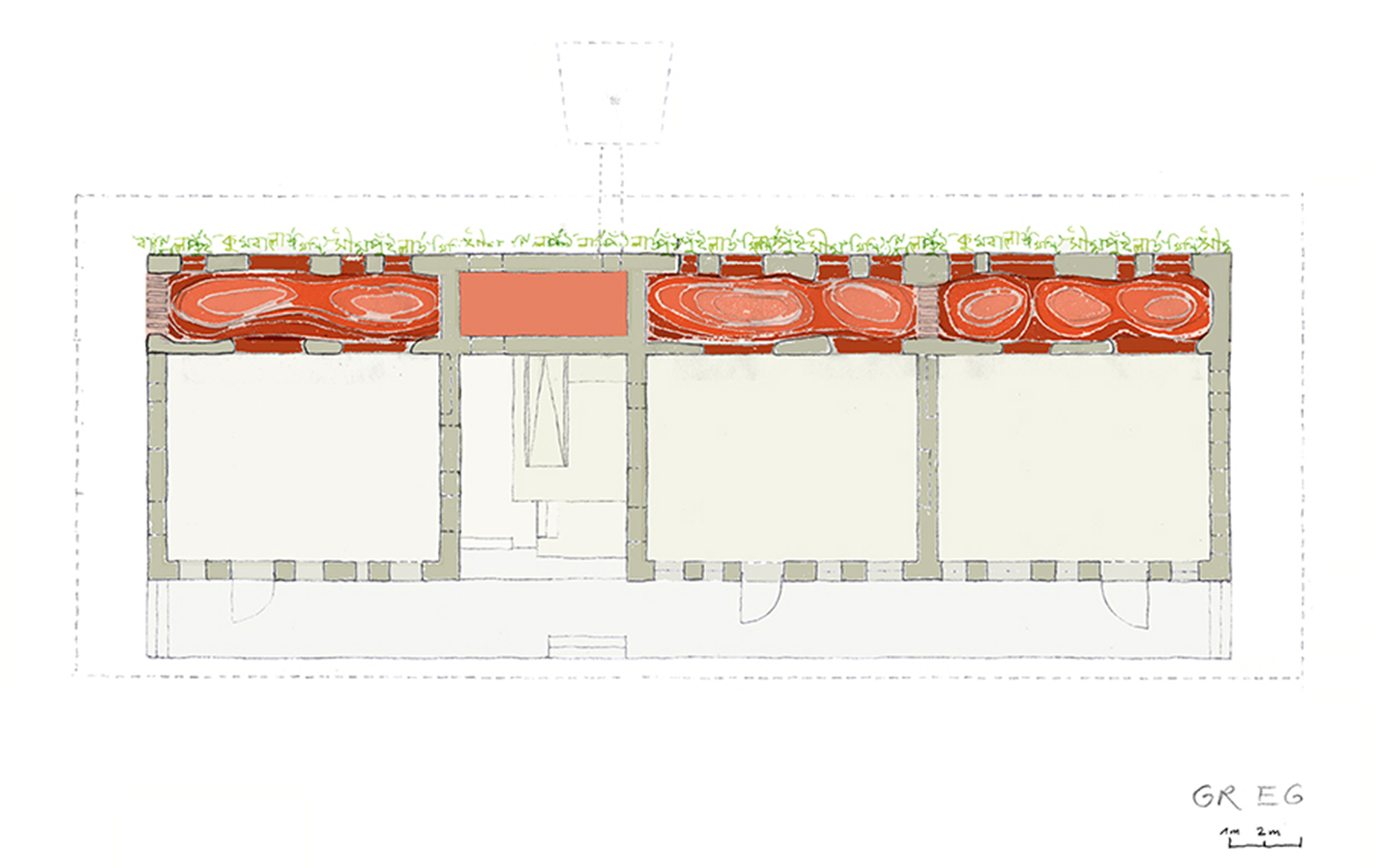
Rudrapur lies in the north of the most densely populated country on the earth. Poverty and the lack of an infrastructure drive many people from the countryside into the cities. The local NGO Dipshikha attempts to follow new paths with its development programme: the intention is to give the rural population perspectives and to help people learn about the value of the village in all its complexity. Part of this is a special school concept that instils in the children self-confidence and independence with the aim of strengthening their sense of identity. The building rests on a 50 cm deep brick masonry foundation rendered with a facing cement plaster. Bricks are the most common product of Bangladesh’s building manufacturing industry. Bangladesh has almost no natural reserves of stone and as an alternative the clayey alluvial sand is fired in open circular kilns into bricks. These are used for building or are broken down for use as an aggregrate for concrete or as ballast chippings. Imported coal is used to fire the kilns.
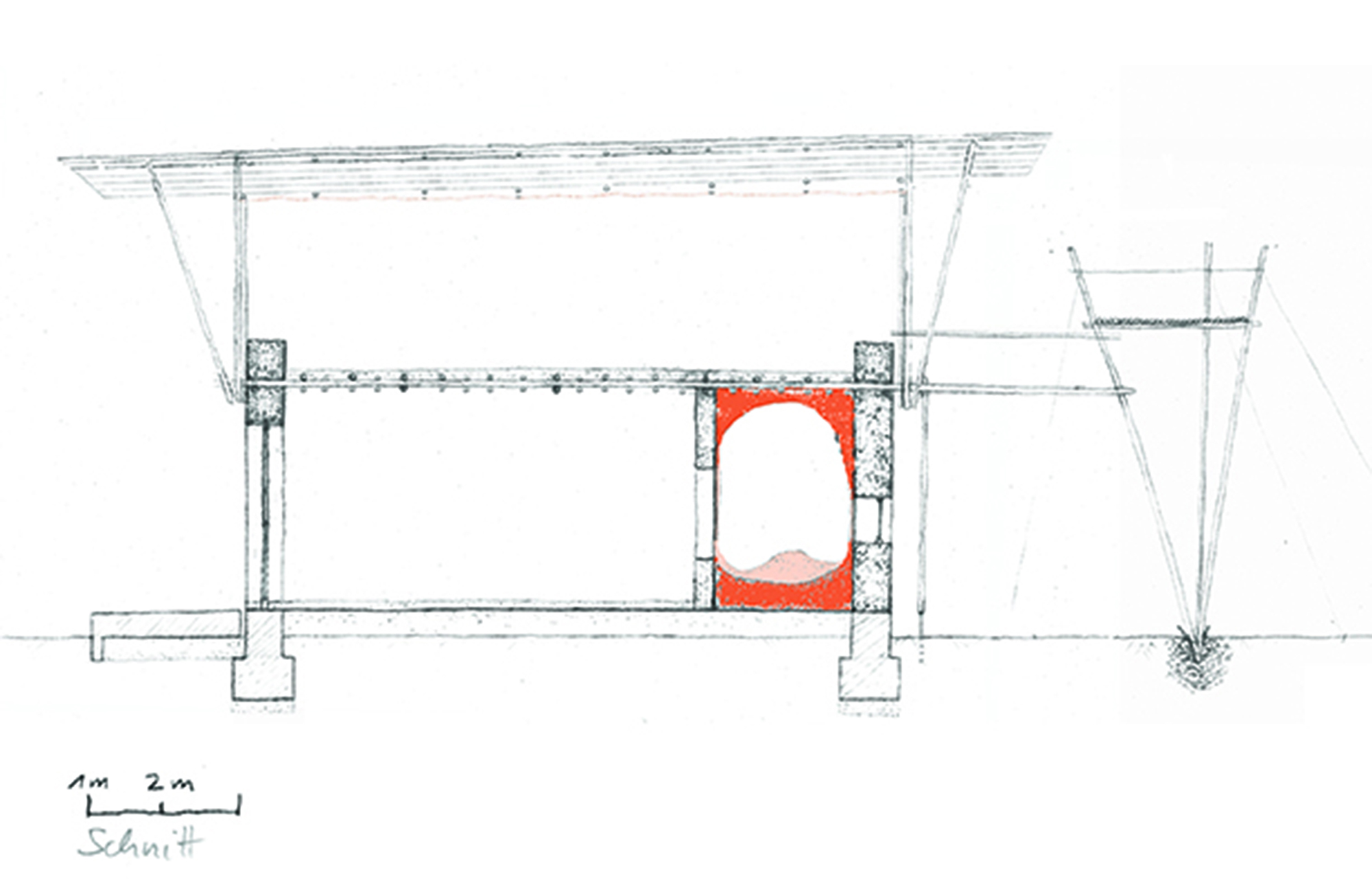
Aside from the foundation, the damp proof course was the other most fundamental addition to local earthen building skills. The damp proof course is a double layer of locally available PE-film. The ground floor is realised as load-bearing walls using a technique similar to cob walling. A straw-earth mixture with a low straw content was manufactured with the help of cows and water buffalo and then heaped on top of the foundation wall to a height of 65 cm per layer. Excess material extending beyond the width of the wall is trimmed off using sharp spades after a few days. After a drying period of about a week the next layer of cob can be applied. In the third and fourth layers the door and window lintels and jambs were integrated as well as a ring beam made of thick bamboo canes as a wall plate for the ceiling.
The ceiling of the ground floor is a triple layer of bamboo canes with the central layer arranged perpendicular to the layers above and beneath to provide lateral stabilisation and a connection between the supporting beams. A layer of planking made of split bamboo canes was laid on the central layer and filled with the earthen mixture analogue to the technique often used in the ceilings of European timber-frame constructions.
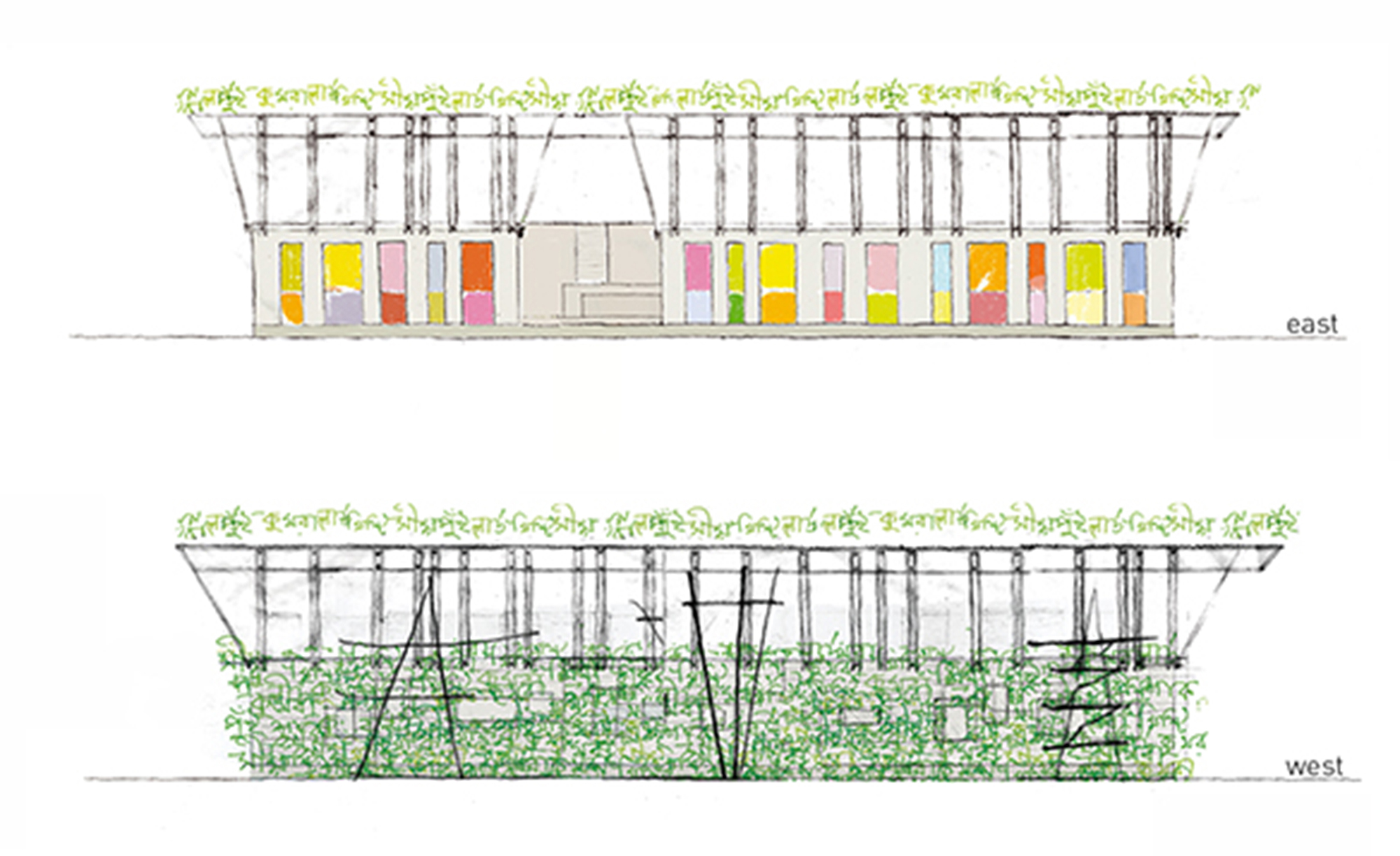
The upper storey is a frame construction of four-layer bamboo beams and vertical and diagonal members arranged at right angles to the building. The end of the frames at the short ends of the building and the stair also serve to stiffen the building. These are connected via additional structural members with the upper and lower sides of the main beams and equipped with additional windbracing on the upper surface of the frame. A series of bamboo rafters at half the interval of the frame construction beneath provide support for the corrugated iron roof construction and are covered with timber panelling and adjusted in height to provide sufficient run-off.
The entire budget for the school construction remained within the village and the direct surrounding: the building materials earth and bamboo were all local as well as the construction workers.
The construction workers were all day-labourers from the village Rudrapur. During the construction process they were trained in improved earth- and bamboo construction techniques.
The building techniques were chosen in order to be able to be replicated by the local people and in order to have a positive effect on the existing, poor housing situations.
The school-kids were involved in the building process as well to learn the value of sustainable construction and to reflect on it.